Unlocking the Trillion-Dollar Opportunity
The Next Trillion-Dollar Software shift: Building and Selling for the Agentic Age-SaaS (2.0) & transitioning from traditional SaaS (1.0) to tap the big opportunity of the next decade.
Standing at the threshold of Transformation
Every decade brings a technological inflection point that fundamentally reshapes the business landscape. Every 20-25 years brings a larger and deeper economic opportunity intertwined with those technological changes.
The early 2000s witnessed the rise of cloud-based software, displacing on-premise solutions with more accessible subscription models. Today, we stand at the threshold of another momentous shift: the evolution from traditional SaaS to AI-powered, agent-led systems that will redefine the core dynamics of how software is conceived, delivered, and experienced.
This isn't about the "sunset of SaaS" – it's about its metamorphosis into something profoundly more powerful, accessible, and business-aligned. Just as cloud software democratized access by eliminating massive upfront costs and technical barriers, AI-powered systems are poised to unlock unprecedented levels of personalization, autonomy, and true outcome-driven value.
Three dimensions to analyse this: the expanding economic opportunity, the revolution in business models toward outcome-based relationships, and the dramatic compression of development cycles through intelligent systems. More importantly, we'll consider how these converging forces are creating a trillion-dollar opportunity over the next 5-10 years for those who embrace this new paradigm with the challenges that will come along.
The Economic Horizon: Untapped Markets and Expanding Possibilities
The financial trajectory of enterprise software has been nothing short of remarkable.
From a market estimated at approximately $100 billion in 2000, the global SaaS ecosystem had expanded to $273 billion by 2023, with projections approaching $300 billion by 2025.
Looking onwards to the next few years, the intelligence-augmented software market is forecast to exceed $900 billion by 2030. This isn't just incremental growth – it represents a fundamental expansion of possibilities and addressable markets. McKinsey's analysis suggests generative AI could contribute $2.6-4.4 trillion annually to the global economy, with software development and business operations among the most profoundly impacted sectors.
What's most compelling about this opportunity is not just its scale but its composition. Despite decades of SaaS evolution, approximately 85% of the world's small and medium-sized businesses operate largely without modern software solutions. In concrete terms, that's over 400 million businesses worldwide still managing with minimal digital infrastructure – an untapped reservoir of potential customers.
Breaking New Ground: Markets on the Verge of Transformation
Three significant market segments have remained largely beyond the reach of traditional software:
The Small Business Ecosystem: With over 400 million SMBs globally, this segment represents a vast untapped opportunity. The fundamental economics haven't aligned until now – these businesses couldn't justify enterprise-level software costs, and vendors couldn't profitably serve them at scale. A 2023 Deloitte analysis revealed that 76% of SMBs identified cost as the primary barrier to adopting sophisticated software solutions .
Emerging Market Acceleration: Regions like India, Southeast Asia, and Latin America have experienced rapid digitization but limited penetration of sophisticated business software. World Bank economic models suggest that improving digital adoption in these markets could contribute $1.5 trillion to their collective GDP by 2030.
Vertical Market Specialization: Niche industries with specialized operational requirements have traditionally been underserved because the economics of developing tailored solutions for smaller audiences didn't compute. Industries like agriculture, construction, specialized manufacturing show digitization rates 40-60% lower than horizontal business functions like accounting or CRM.
The Intelligence Differentiator
The critical catalyst for this market expansion is the embedded intelligence now being integrated throughout the software stack. Each block of the ecosystem is becoming more intelligent. AI fundamentally alters the economics of software delivery in three dimensions:
Implementation Cost Reduction: Conventional SaaS deployment costs typically range from 1.5x to 3x the annual subscription fee. AI-enhanced solutions can reduce this overhead by 40-60% through automated configuration, intelligent data migration, and personalized setup processes.
Adoption Acceleration: User training and organizational adoption historically account for 30-40% of total implementation costs. Natural, adaptive interfaces that conform to user preferences rather than forcing standardization can dramatically reduce this friction.
Value Realization Amplification: According to Bain's 2023 analysis, nearly two-thirds of enterprise customers fail to realize the full expected value from their SaaS investments. AI systems that continuously optimize for business outcomes can potentially close this value gap through ongoing adaptation and enhancement.
The implications extend far beyond incremental efficiency gains. We're witnessing the emergence of software that intuitively understands business context, delivers enterprise-grade capabilities at SMB-friendly economics, and adapts to organization-specific needs rather than forcing standardization – all fundamental prerequisites for unlocking the next trillion dollars of market opportunity.
Beyond Features: The Commercial Revolution in Software
The commercial transformation unfolding in the software industry represents perhaps the most significant shift in business models since the move from perpetual licenses to subscriptions two decades ago.
The modern software industry has traditionally operated on a fundamental gap: organizations pay for features and capabilities, not business outcomes. Traditional software required substantial upfront investment regardless of whether it delivered measurable value. SaaS improved this dynamic with subscription models, reducing initial risk. However, customers still primarily paid for access to functionality, not guaranteed results.
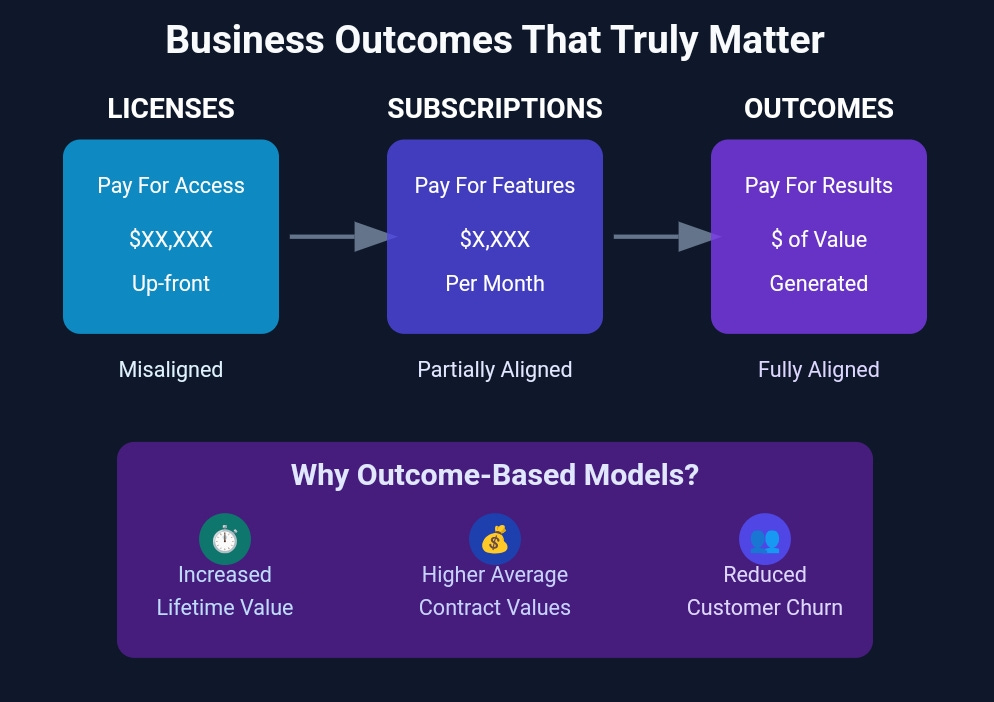
The Commercial Evolution: From Access to Outcomes
The License Era: Purchasing Potential
Capital expenditure model with substantial upfront investment
Typical enterprise costs ranging from $100,000 to multi-millions
Disconnected from actual value realization passing the risk to buyers
Conventional enterprise systems often required implementation investments averaging 5-7x the software license cost
The Subscription Revolution: Accessing Capabilities
Operational expenditure model with recurring payments
Monthly/annual fees typically ranging from thousands to tens of thousands
Partially connected to value through retention requirements
Modern enterprise platforms still experience high monthly churn despite extensive Customer Success programs
The Outcome Transformation: Investing in Results
Value-based commercial model with payment tied to measurable impact
Investment directly proportional to demonstrated return
Fundamentally aligned with customer’s true commercial success their business metrics
The Business Impact: Early Signals of Value
Organizations pioneering outcome-based commercial models are already demonstrating significant advantages:
Enhanced Customer Lifetime Value: Businesses implementing outcome-based pricing have documented 40-60% increases in average customer lifetime value compared to traditional subscription arrangements.
Expanded Contract Values: Outcome-based agreements typically generate 25-35% higher average contract values than comparable subscription structures.
Strengthened Retention Metrics: Organizations utilizing outcome-based pricing report 30-50% lower customer churn rates than industry benchmarks for subscription models.
Pioneers of the Outcome Economy
Innovative outcome-based commercial models are emerging across various domains:
Performance Marketing Technology: Platforms charging based on attributable revenue generation rather than flat subscription fees. Companies like Clearbit and select Shopify partners have pioneered this approach, with customer satisfaction ratings 35% higher than industry benchmarks.
Resolution-Based Support: Solutions charging per successful issue resolution rather than per agent seat. Zendesk's experimental implementations have shown 28% improvements in customer satisfaction alongside 15% reductions in overall support costs.
Impact-Driven Analytics: Platforms charging based on measurable financial impact rather than access to capabilities. Alteryx and certain Tableau implementation partners have adopted this model, documenting 3-5x ROI improvements compared to traditional licensing structures.
The Horizon: Emerging Models of Value Alignment
The next wave of outcome-based commercial relationships is extending into new territory:
Pipeline-Based Sales Enablement: Transitioning from fixed subscription fees to percentage-based compensation tied to incremental pipeline generation.
Efficiency-Driven Inventory Management: Moving from flat platform fees to performance-based pricing tied to measurable reductions in carrying costs and stockouts.
Savings-Aligned Procurement: Evolving from access-based subscriptions to success fees calculated on negotiated savings secured through the platform.
Conservation-Based Facility Management: Shifting from system licensing to performance agreements based on documented utility cost reductions.
Proficiency-Centred Learning: Transforming from seat-based pricing to models aligned with measurable skill acquisition and retention.
This commercial revolution fundamentally requires AI because monetizing outcomes demands software that can understand, measure, and actively participate in customers' business processes at unprecedented depth. McKinsey projects that by 2028, 30-40% of enterprise software agreements will incorporate outcome-based components.
Building and Delivering Software: From Months to Minutes
Perhaps the most profound transformation underway is the fundamental reimagining of how software itself is created, evolved, and enhanced.
The traditional development lifecycle has progressed from waterfall to agile methodologies, but even the modern agile approaches remain constrained by human limitations:
Customer feedback collection (days / weeks)
Prioritization and planning (weeks / months)
Development and testing (weeks / months)
Deployment and iteration (weeks / months)
This inherent cycle time has been a critical constraint in delivering truly responsive software, particularly for organizations with unique requirements or limited resources.
The Agentic Paradigm: Continuous Evolution Through Intelligence
The emergence of agentic development systems is dissolving the boundaries between feedback, development, and deployment into a continuous, intelligent process:
Continuous Conversational Feedback (minutes): AI systems engage with users across all touchpoints, constantly gathering input and usage patterns to inform enhancement opportunities.
Automated Requirement Translation (seconds): Natural language processing transforms user observations and suggestions into structured technical requirements without human interpretation delays.
Intelligent Priority Orchestration: AI systems evaluate enhancement opportunities against business impact, user value, and implementation complexity to optimize development resources.
Accelerated Development Cycles (minutes to hours): Generative AI produces, tests, and refines code at speeds orders of magnitude faster than traditional approaches.
Seamless Deployment Pipelines (hours): Changes are automatically implemented with sophisticated guardrails and monitoring to ensure quality and stability.
According to Forrester's 2023 analysis, organizations adopting AI-augmented development practices are experiencing 3-5x improvements in deployment frequency and 70-80% reductions in time-to-implementation for customer-requested enhancements.
The Foundations to build: Four Pillars of Agentic Software
The transformation toward agentic systems rests on four core capabilities:
Contextual Understanding and Adaptation: Software that comprehends individual usage patterns and organizational context, adapting itself accordingly. Early implementations have demonstrated 40-60% improvements in engagement and productivity metrics.
Continuous Self-Optimization: Systems that evolve based on usage patterns without explicit programming. Organizations implementing these capabilities have documented 25-35% reductions in support requirements and training costs.
Pre-emptive Issue Resolution: Applications that identify and address potential problems before users encounter them. Initial deployments have shown 50-70% reductions in reported issues and system disruptions.
Dynamic Development Prioritization: Enhancement roadmaps that adjust in real-time based on actual usage patterns and business impact rather than predetermined schedules. Companies employing these approaches report 30-40% higher feature adoption rates.
The Transformative Impact
The implications for both creators and consumers of technology are profound:
Exponential Velocity: Development cycles compressed by orders of magnitude, transforming months into days or hours. GitHub's Copilot has already demonstrated productivity improvements of 55% for developers across a range of coding tasks.
Individual Relevance: Solutions that adapt to specific organizational contexts rather than forcing standardization. Companies implementing personalized experiences have seen adoption rates improve by 35-45%.
Anticipatory Resolution: Issues identified and addressed before most users even become aware of them. Tesla's autonomous testing systems now identify and resolve 90% of potential issues before customer exposure.
Organic Evolution: Interfaces and workflows that continuously optimize based on usage patterns. Google's experiments with AI-enhanced interfaces have shown 20-30% improvements in task completion rates.
Consider this real-world scenario: A finance manager casually mentions to a support AI Agent, "It would be helpful if I could allocate this invoice across multiple departments." Within hours – not weeks or months – that capability is designed, implemented, tested, and deployed specifically for that organization. This represents a fundamental shift from software as a static product to software as a living system that continuously evolves in response to its users.
Navigating all of this: Key Challenges
There is no free lunch. Every new massive opportunity comes with it’s own challenges. While the opportunity is immense, organizations seeking to capitalize on this transformation face several critical challenges:
1. Organizational Readiness and Culture
The shift from traditional development and sales models to AI-augmented, outcome-based approaches requires significant cultural adaptation. 68% of digital transformation initiatives fail due to organizational resistance rather than technical limitations, says a 2023 BCG study.
Key Considerations:
Cultivating a culture that embraces continuous change and evolution
Developing new skills and competencies across development, sales, and customer success teams
Establishing new metrics and incentives aligned with outcome-based models
2. Ethical and Responsible AI Integration
As AI becomes increasingly embedded in mission-critical systems, organizations must address complex ethical considerations. 72% of consumers express concerns about AI ethics and safety in the software they use, Deloitte survey found in a survey in 2023.
Key Considerations:
Ensuring transparency in how AI systems make decisions and recommendations
Establishing robust governance frameworks for AI deployment and evolution
Addressing potential biases and unintended consequences in AI-driven systems
3. Technical Complexity and Integration
Implementing agentic systems requires sophisticated technical infrastructure and integration capabilities. 60% of organizations struggle with the technical complexity of AI integration into existing systems, claims McKinsey.
Key Considerations:
Building flexible, modular architectures that can evolve continuously
Addressing data quality and accessibility challenges
Establishing robust security and privacy frameworks for AI-powered systems
4. Customer Adoption and Trust
Moving customers to outcome-based models requires building significant trust and demonstrating verifiable value. Gartner notes that 55% of enterprises express concerns about the measurability and verification of outcomes in value-based contracts.
Key Considerations:
Developing transparent, mutually agreeable measurement frameworks
Creating transitional models that bridge traditional and outcome-based approaches
Building case studies and reference customers demonstrate trust based adoption and deeply sharing wins and losses together for proven value
5. Competitive Landscape
Early movers in this transformation will gain significant advantages, but the landscape is evolving rapidly. Over 80% of enterprise software vendors are actively exploring AI-powered capabilities and new business models, according to IDC.
Key Considerations:
Identifying and securing key AI talent and capabilities
Developing unique IP and differentiation in AI-powered experiences
Establishing strategic partnerships to accelerate transformation
The Convergence of Opportunity
The three dimensions of transformation – market expansion, business model evolution, and development acceleration – are not isolated trends but interconnected forces that amplify each other:
Expanded markets enable outcome-based models: As AI reduces the cost to serve previously unprofitable segments, it becomes economically viable to offer outcome-based arrangements to businesses of all sizes.
Outcome alignment drives development acceleration: When commercial success is tied directly to customer outcomes, organizations have powerful incentives to rapidly deploy capabilities that drive measurable value.
Accelerated development unlocks new market segments: The dramatic reduction in development and customization costs allows profitable service to segments that were previously uneconomical to address.
Incumbents vs Upstarts
All of these present a bigger challenge for the incumbents to transition while the AI-native start-ups can adapt sooner and quicker instead of following traditional playbooks. This would mean the inroads can be made by newer providers but can they hold on to their turn as the enterprise providers adapt and come in with better solutions and better packing of commercial offerings once the younger providers have opened some of these markets?
The organizations that will define this next era will be those that recognize and harness these interconnected transformations. They won't simply build better AI features – they'll fundamentally reimagine how software is conceptualized, delivered, and experienced.
This isn't about the end of SaaS – it's about its evolution into something significantly more valuable, accessible, and aligned with business impact leading to a much deeper integration into our world.
The winners in this transformation won't just be those with the most advanced algorithms or the largest data sets, but those who most effectively harness these capabilities to unlock previously impossible value for their customers.
The unlocking of the trillion-dollar opportunity is starting, and it will be as transformative as the shift from on-premise to cloud was two decades ago. The question isn't whether this transformation will happen, but who will lead it and how!
PS. The write-up is certainly prepared with the help of AI assistants for research, ideas brainstorming, data collection and proof reading.